CURRICULA TRAINING ACTIVITIES

PREHISTORY
Prehistory – the main objective is to provide appropriate knowledge for man’s biological and evolutionary reconstruction within his environment and culture. The aim of study is to define and interpret behaviors and sustenance strategies during our complex evolutionary process.
ACTIVITIES’ TRAINING CONTENT
Biologic and cultural evolution; prehistoric ecology; chronology and cultures of Early, medium and late Paleolithic, of the Mesolithic, of Neolithic up to the age of metals; inorganic rough materials supply and circulation; Prehistory in Europe, Asia, Oceania, America and Africa; lithic technology, ethnology and archeology, symbolic behavior archeology
PALEOANTHROPOLOGY
Paleo-anthropology – the necessary interdisciplinary approach to anthropological aspects of man’s evolution will be provided within curricula. A sort of continuity between our species’ early and present behavior will be established.
ACTIVITIES’ TRAINING CONTENT
Human paleontology and paleo-anthropology; genetics of populations; language evolution; human skeleton’s biology; human genetics; genetics evolution; human language and animal communication; knowledge processes’ psychology; Primates and environment; human paleontology and ecology; central nervous system evolution in anthropology.

METHODOLOGY
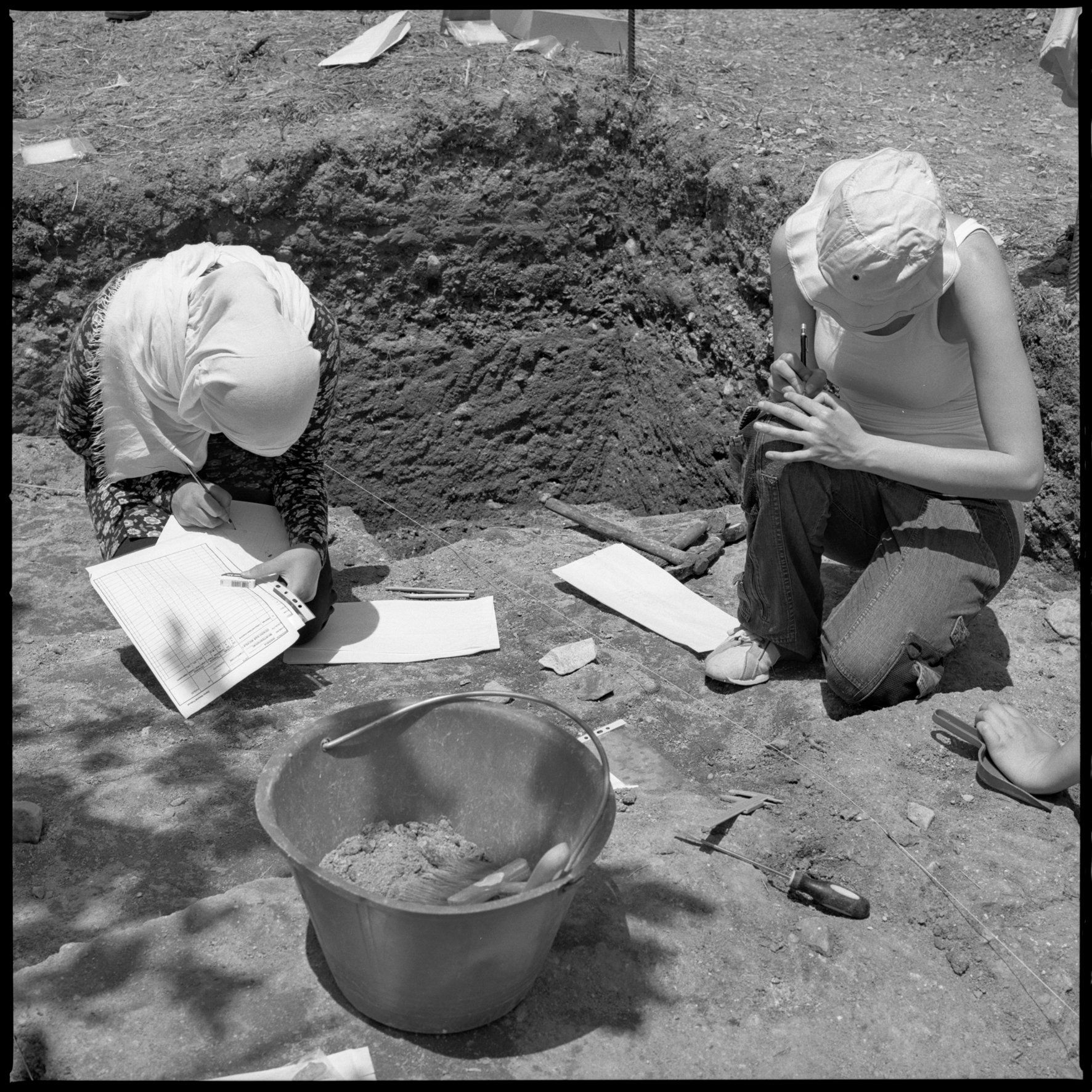
Procedures for research on prehistory and archeology – the objective is to provide the necessary practical and theoretical skills for archeological evidences management and interpretation. The field of prehistoric archeology is extremely wide and needs an interdisciplinary and well balanced kind of approach and in order to collect all necessary data for the documentation and the consequent interpretation of archeological evidences.
ACTIVITIES’ TRAINING CONTENT
A rcheo-zoology and taphonomy (?) of animals’ hard materials; anthropoid and paleontology deposits’ genesis and evolution; functional lab analysis of lithic material; Technology and lithic technology lab; dating radiometric; archeological excavation methods and techniques lab; laboratory for the ecology and the tassonomy of the malacofauna; vertebrate anatomy lab; birds and mammals paleontology lab; archeo-zoology experimental lab; informatics and statistics applied to archeology; on site archeology lab; info elaboration and 3D; experimental archeology; GIS.

GEOLOGY AND PALEONTHOLOGY
Geology and Paleontology of Quaternary – the objective is to provide necessary knowledge on the interpretation of geologic/environmental context within prehistoric settlements. The multidisciplinary approach including geological, paleontological and biological aspects will allow to draw a complete scene of the study on prehistory and Quaternary.
ACTIVITIES’ TRAINING CONTENT
Vertebrate evolution; Quaternary’s fauna evolution; Quaternary’s vegetable evolution; geo-archeology of prehistoric archives; geology and stratigraphy of continental formation; vertebrate zoology; ethology.

HERITAGE PRESERVATION
Heritage preservation and revaluation - the objective to provide all necessary practical and theoretical knowledge for the preservation of our archeological heritage. The revaluation process is a very important opening for work opportunities. The aim is to enable doctors to recognize, study and interpret the cultural heritage always in the attempt to preserve, to revaluate and to disclose it.
ACTIVITIES’ TRAINING CONTENT
Paleontological restoration; biology of preservation; microclimate for the preservation; legal system and cultural heritage; epistemology and science history; prehistoric heritage revaluation and management.

QUATERNARY AND PREHISTPRY
The International Master in Quaternary and Prehistory (IMQP) offers an interdisciplinary curriculum that combines archaeology, geology, and anthropology to explore human evolution and cultural development.
Practical training includes fieldwork at archaeological sites, laboratory analyses, and the use of advanced technologies like GIS and AI in prehistory research.
The program is hosted by leading institutions across Europe, providing a truly international perspective on the Quaternary and Prehistory, with a strong focus on both academic research and professional skills.
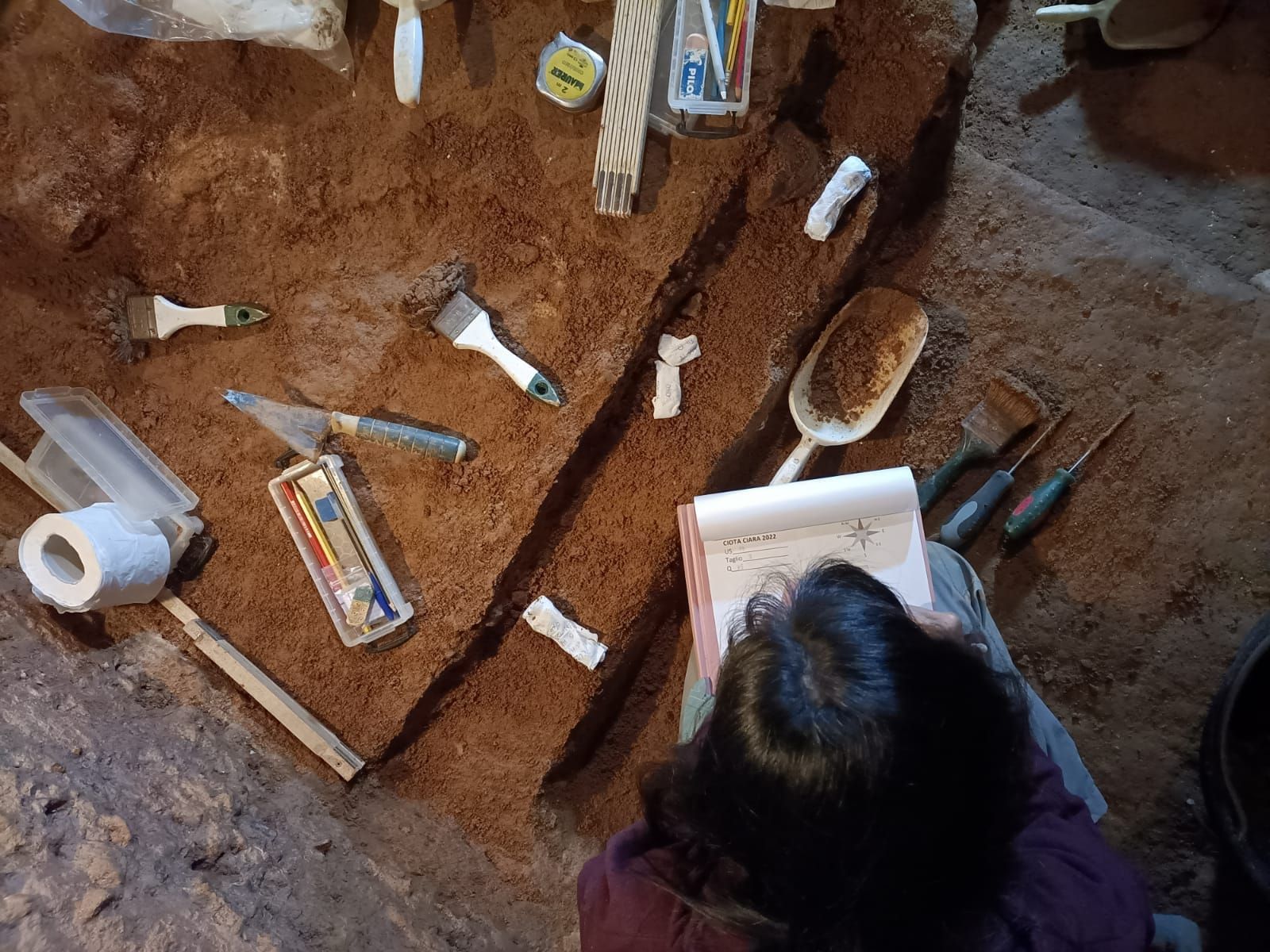

Stages and Excavations
Students can carry out their internships at the excavation sites of partner institutions or in laboratories at full partners and associated partners. It is also possible to conduct the internship at external institutions, subject to agreement with their tutor.



